Fire Doors Research Field: Analysis of Fire Resistance Performance of Fire Doors and Fire Shutters
“Fire doors” Authors: Liu Zhipeng, Zhang Yulin, Zhang Zheng, Li Bo,(1. Guangdong Product Quality Supervision and Inspection Research Institute; 2. Guangdong Provincial Fire Brigade)
Abstract: The fire resistance performance ofBlaze-rated door and fire shutters is a critical indicator for evaluating their quality. Sufficient fire resistance time can significantly delay the spread of fire. This study analyzes test results from sampled Fire-rated entry door and fire shutters to identify factors affecting their fire resistance performance, proposing practical measures for improvement.
As urban development accelerates, the demand for fire safety measures in buildings has surged, particularly with the increase in high-rise structures. Fire-safety door, recognized for their role as passive fire protection devices, can effectively contain flame and smoke within a designated area during a fire incident. This containment is essential, especially in densely populated residential areas and large public venues, where the ability to delay the spread of fire can save lives and minimize property loss.
Understanding Fire Doors and Fire Shutters
Fire doors are specifically designed to meet strict fire resistance standards. According to GB/T 9978.1-2008, Combustion-rated door must pass rigorous testing to achieve compliance with GB 12955-2008. These standards categorize Flame-rated door based on their operational mechanisms and materials used in their construction.
- Types of Fire Doors:
- Closed Fire Doors: Typically remain closed, requiring manual operation to open. Comprising a door leaf, frame, and various hardware, these doors are prevalent in the market, making up over 90% of all fire doors in use.
- Open Fire Doors: Designed to remain open under normal conditions but automatically close during a fire event. These doors are equipped with advanced systems that respond to fire alarms, ensuring effective containment.
- Materials Used:
- Steel Fire Doors: Constructed with a steel frame and filled with non-toxic fire-resistant insulation materials, these doors offer robust protection.
- Wooden Fire Doors: Made from fire-retardant wood or wood products, ensuring that the door’s core remains fire-resistant while being aesthetically pleasing.
- Steel-Wood Composite Fire Doors: Combine the benefits of both materials to enhance fire resistance.
Technical Requirements for Fire Resistance Performance
Fire doors are classified according to their thermal insulation properties, as outlined in GB 12955-2008:
- Type A (Insulated Fire Doors): High-level fire resistance, capable of maintaining structural integrity for extended periods.
- Type B (Partially Insulated Fire Doors): Moderate insulation properties.
- Type C (Non-Insulated Fire Doors): Limited insulation capabilities, primarily used where fire risk is lower.
This structured analysis not only highlights the essential characteristics of Blaze-rated door and shutters but also underscores the importance of heat resistance in enhancing safety standards in modern buildings. By leveraging the expertise of Guangdun Door Industry Co., Ltd., we aim to contribute to the ongoing dialogue surrounding fire safety and building materials, reinforcing our commitment to excellence as one of the leading fire door manufacturers in the industry.
Fire Doors and Fire Shutters: Key Components for Horizontal Fire Separation
Fireproof door and fire shutters serve as essential components for fire separation in buildings, particularly in high-rise structures, large shopping malls, warehouses, factories, underground garages, and hotels, where high occupancy is common. They play a vital role in preventing the spread of fire and minimizing fire-related losses. The fire resistance performance of these installations is a critical indicator of their effectiveness.
Recent quality inspections of Fireproof door and fire shutters have revealed concerning trends in the construction and market sectors, with a significant number of products failing to meet established fire-resistance standards. Identifying the factors that affect the fire resistance performance of these products is therefore crucial for enhancing overall product quality.
Types of Fireproof door and Fire Shutters

According to GB 12955-2008, Fireproof door are classified based on their flame resistance performance into three categories:

- Type A (Insulated Fire Doors): These doors have specific requirements for both thermal insulation and structural integrity.
- Type B (Partially Insulated Fire Doors): These also need to meet certain standards but have moderate insulation properties.
- Type C (Non-Insulated Fire Doors): These are primarily evaluated on their integrity and have no insulation requirements.
The fire resistance durations for these door types are categorized as follows:
- Class A: 1.5 hours
- Class B: 1.0 hour
- Class C: 0.5 hours
Currently, steel fire doors are the most widely used option.
Fire shutters are classified based on their fire resistance limits:
- Steel Fire Shutter (GFJ): High fire resistance capabilities.
- Steel Fire and Smoke Shutter (CFYJ): Offers protection against both fire and smoke.
- Inorganic Fiber Composite Fire Shutter (WFJ): Utilizes inorganic materials for enhanced fire resistance.
- Inorganic Fiber Composite Fire and Smoke Shutter (WFYJ): Combines fire and smoke protection features.
- Special Fire Shutter (TFJ): Designed for high-performance requirements.
Fire resistance durations for fire shutters include ≥ 2.00 hours and ≥ 3.00 hours. The most common types in use today are steel fire shutters and inorganic fiber composite fire shutters.
National Standards for Fire Resistance Limits of Fire Doors and Fire Shutters
The “Code for Fire Protection of High-Rise Civil Buildings” (referred to as “High-rise Code”) outlines specific fire resistance requirements for fire doors and fire shutters:
- Article 4.2.4: When two high-rise buildings are adjacent or when a high-rise building is next to a non-high-rise building of at least Level II fire resistance, the fire distance can be reduced (but not below 4.00 meters) if the higher building’s exterior wall has a fire resistance limit of no less than 2.00 hours, and has Class A fire doors, windows, or fire shutters in its openings.
- Article 5.1.4: When high-rise buildings have connected corridors, open stairs, escalators, etc., the upper and lower floors should be treated as a single fire separation zone. If fire shutters or water curtains with a fire resistance limit greater than 3.00 hours are installed, their area may not be included in the cumulative building area calculation.
- Article 5.1.5.2: Passages and corridors that connect to atriums should be separated by Class B fire doors or fire shutters with a fire resistance limit greater than 3.00 hours.
- Article 5.4.4: In locations where it is difficult to install fire walls, fire shutters may be used for fire separation. This includes managing the temperature rise on the non-fire side of the fire barrier.
By analyzing the structural and regulatory landscape surrounding fire doors and fire shutters, Guangdun Door Industry Co., Ltd. emphasizes its commitment to producing high-quality fire-rated doors that meet stringent safety standards. Our academic foundation and technical expertise position us as a leader among fire door manufacturers, ensuring that our products effectively contribute to fire safety in various building types.
Fire Resistance Conditions for Fire Shutters
When establishing fire resistance limits for fire shutters, the conditions dictate that the resistance must be no less than 3.00 hours. In cases where the determination of fire resistance does not include the temperature rise on the non-fire side, the fire shutter must be protected by independently operating closed automatic sprinkler systems on both sides. The duration of the sprinkler operation must not be less than 3.00 hours.
According to the High-rise Code, the following specifications are noteworthy:
- Article 6.3.3.4: The doors leading to the fire elevator lobby should use Class B fire doors or fire shutters equipped with a holding function.
From these regulations, it is clear that fire doors are typically required to meet at least Class B standards (fire resistance time of 1.0 hour), while fire shutters generally require a fire resistance duration exceeding 3.00 hours.
Testing Procedures
This study follows GB/T 9978.1-2008 “Fire Resistance Test Methods for Building Components Part 1: General Requirements” and GB 12955-2008 “Fire Doors” to assess the fire resistance of different types of fire doors. The heating curves within the furnace and the pressure conditions are illustrated in Figures 1-3
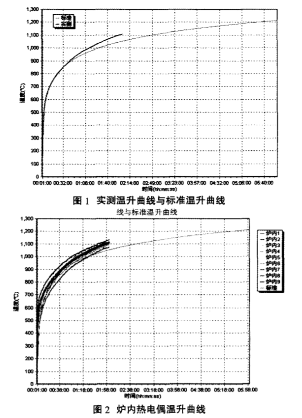
Current Status of Fire Doors and Fire Shutters
In a 2011 special supervision survey conducted in a certain province, data revealed concerning trends in fire door quality. A total of 50 fire doors were randomly sampled from both production and usage sectors, adhering to the testing standards outlined in GB/T 7633-2008 “Fire Resistance Test Methods for Doors and Shutters.” The fire resistance tests utilized the Warrington fire component testing furnace. Among the samples, 31 were steel fire doors, 10 were wooden fire doors, and 10 were made of other materials. Alarmingly, the overall compliance rate stood at only 44%. Furthermore, fire shutters rarely achieved the standard requirement of 3.00 hours of fire resistance. This data highlights a significant quality concern for both fire doors and fire shutters.
Analysis of Non-compliance in Fire Resistance Time
Fire integrity is defined as the ability of a building component to prevent the penetration of flames and hot gases during a standard fire resistance test when one side is exposed to fire. According to CR/T 9978.1-2008 “Fire Resistance Test Methods for Building Components Part 1: General Requirements,” a test specimen is deemed to have lost integrity if any of the following occurs:
- The cotton pad ignites based on the conditions outlined in section 8.4.1.
- A gap probe can pass through according to section 8.4.2.
- Flames appear on the non-fire side and persist for more than 10 seconds.
Practical fire tests indicate that the primary failure points for Combustion-rated door occur at the seams between the door frame and the door leaf, as well as at the fire glass and lock points. In some cases, the cotton pad ignites, while in others, flames break through. Conversely, the majority of non-compliant fire shutters primarily lose fire insulation rather than integrity (see Table 1).
Table 1: Reasons for Non-compliance
| Item | Non-compliance Reason |
|---|---|
| 1 | Warping of door leaves causes flames to escape and ignite the cotton pad. |
| 2 | Exceeding dimensional tolerances between the door frame and leaf leads to excessive gaps, allowing flames to penetrate. |
| 3 | Use of substandard fire glass that shatters under high temperatures, enabling flames to escape through gaps. |
| 4 | Deformation of double-leaf fire doors creates cracks at the seam, allowing hot gases to ignite the cotton pad. |
| 5 | Low expansion rates of sealing strips fail to provide adequate sealing, resulting in hot gas leakage or flame escape. |
| 6 | Insufficient thickness of shutter steel plates leads to deformation at high temperatures. |
Fire insulation is defined as the ability of a building component to maintain the temperature on the non-fire side within specified limits during a standard fire test. According to GB/T 7633-2008, for specimens that include various insulation zones, each zone must be evaluated separately. Loss of fire insulation is confirmed if any one zone fails the following conditions:
- The temperature rise on the non-fire side exceeds an average of 140°C.
- The maximum temperature rise on the back of the door leaf exceeds 180°C.
- The maximum temperature rise on the back of the door frame exceeds 360°C (see Table 2).
Conclusion and Future Directions
Given the current state of quality in fire door and fire shutters concerning their fire integrity and insulation capabilities, coupled with the identified reasons for non-compliance, it is essential to implement the following improvements:
This detailed analysis underlines the significance of adhering to fire safety standards and maintaining the integrity of fire-rated doors. Guangdun Door Industry Co., Ltd. is committed to enhancing product quality by focusing on rigorous testing and compliance with national standards, ensuring the safety of occupants in various high-risk environments.
The British fire door industry has always been at the world’s leading level. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact me or my business partners.
